Nuclear Instrumentation Lab
Tony DiMauro
Home
Radon Lab
1) In this lab we want to measure the radon in our homes. We are using
NaI scintillation detector in the lead vault with the macintosh MCA.
2) The vault is used to keep the background as low as possible.
3) We counted the background radiation for 10 minutes inside the vault
with no radon exposure.
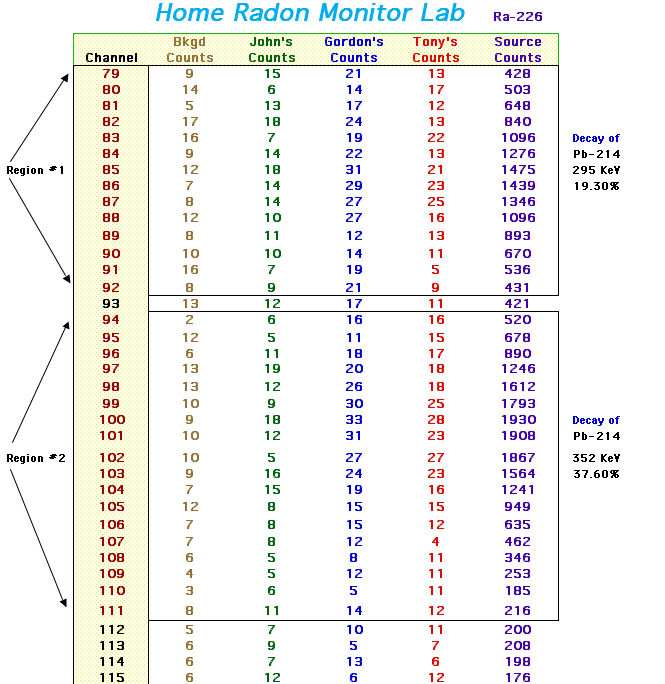
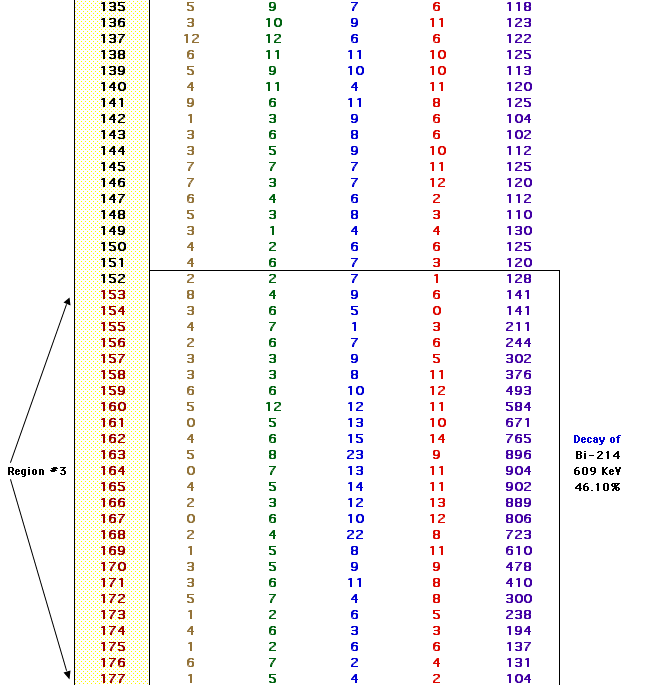
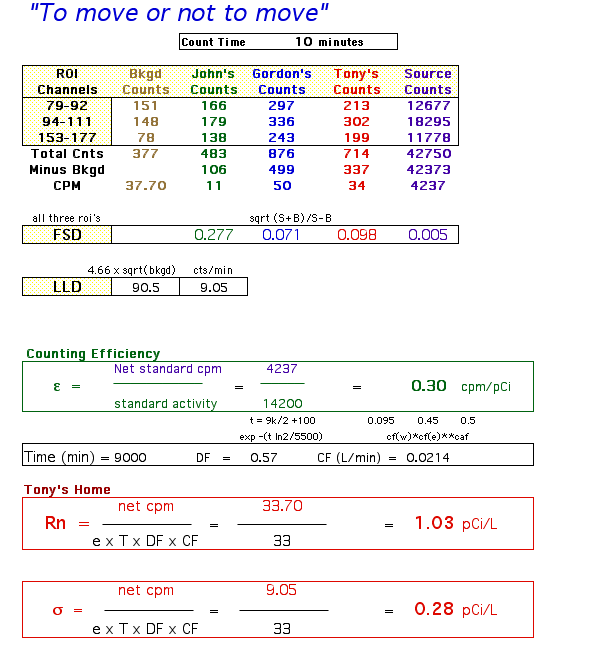
4) We counted a standard source of Radium-226 for 10 minutes. We needed
to do this to be able to calculate the efficiency of the system.
5) We measured the mass of our charcoal canisters before and after placing
them in our homes. This was done to calculate calibration factors involved
in determining the pCi/L.
6) We noted the amount of time exposed for the same reason.
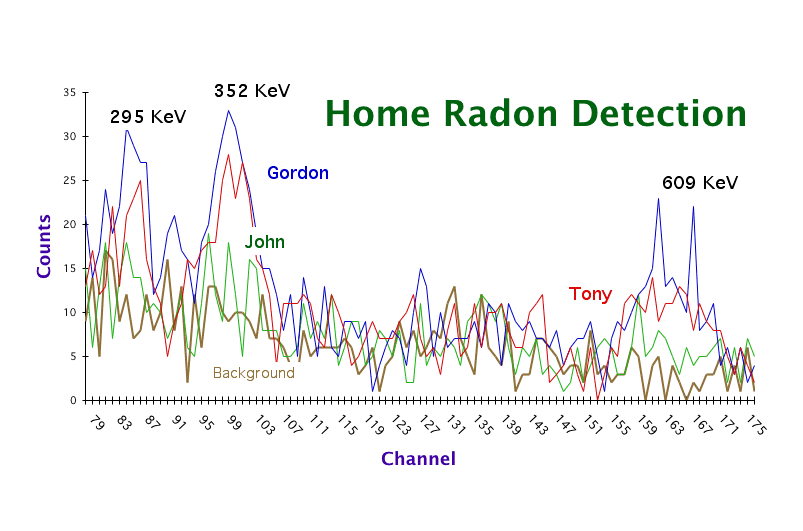
7) We then, counted the radon progeny gammas with the detector for 10
minutes to find the amount of radon that was in our homes.
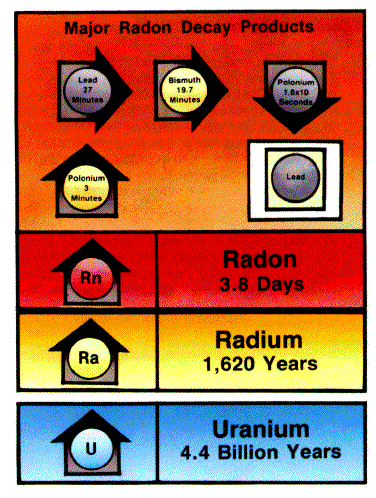
The value that I obtained for the amount of Radon in my crawl space was sensitive to the calibration factors. Changing the calibration factors by a small amount caused the radon concentration to changed abruptly. The CF values that are determine by the amount of water absorption, the exposure time and the CAF should be obtained with great accuracy. Having said that, it was really interesting to realize that we were using radon progeny to calculate Radon itself. The half-lives for the daughter products were very short (~23 minutes). We were suppose to read our canisters four hours after sealing them, but I was not able to measure it for 7 hours. That would have lowered my count by a large factor.
Radon Debate in Radio Biology