On
Intelligence
by
Jeff Hawkins and Susan Blakeslee
Patterns of spatial and temporal
electrical signals are the most
fundamental currency of intelligence.
The Senses 1,2,3
The Brain 1,2,3

Electrostatic
Interactions
The Electric Field
Electric Charges
Electric Force

What
is Electricity?


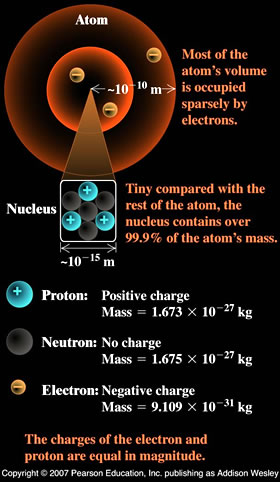
The atom is mostly
space!
Each atom is as old as the universe!
Mechanical Universe - Electric Charge

Like
and Unlike Charges
Positive and Negative Charges

Every material in the world can be defined in terms of how well it conducts electricity
Certain things, such as cold glass, never conduct electricity. They're known as insulators. Materials which do conduct electricity, like copper, are called conductors. In the middle are materials known as semiconductors, which don't conduct as well as conductors, but can carry current. Last, are materials called superconductors, which when brought down to very low temperatures turn into superhighways of current -- they conduct electricity without any resistance whatsoever.


Watch the House get zapped!
How does Lightning relate to electrostatics?
A cool Flash

What did J.J. Thompson say about the electron---listen to it?
in our minds. . .

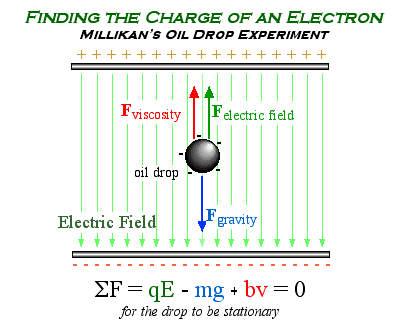
Millikan's
Oil Drop Experiment
What was measured by Millikan?
Was
it easy?

How many electrons in one Coulomb?

The magnitude F of the Force that each of two point charges q1 an q2 a distance r apart exerts on the other is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversly proportional to the square of the distance between them.
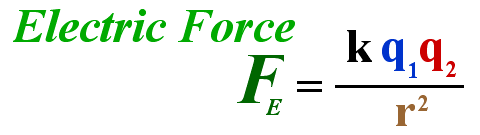

Coulomb
found that the electric force is proportional to

When
the distance doubles,
the force decreases to a fourth of its initial value.
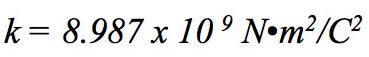
How does the Electric Force compare to The Gravitational Force? Use an electron for an example.
What if one was to triple the separation distance. . .what would happen to the force?
What if one was to cut the separation distance in half?
How was the constant k found?




Gravitational
Forces
-vs-
Electrical Forces
google
fights!



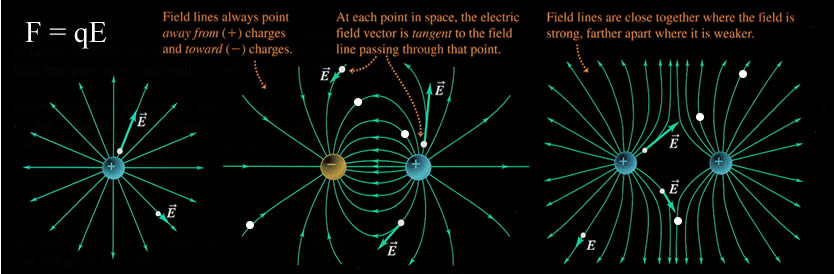
We need to explain how charges 'talk' to each another charge.
So, we invent an Electric Field Lines!
Electric Field lines always begin on positive charges
and end on negative charges.
Electric Field lines communicate to other charges 'how to move'
in the presence of another charge.
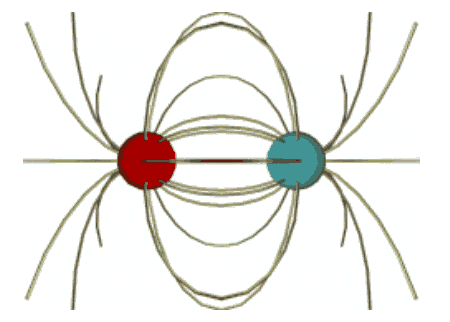

Is the Electric Field real? Or, did we create it out of 'thin air'?




An iTunes Podcast
Electric Fields and healing wounds?

Process

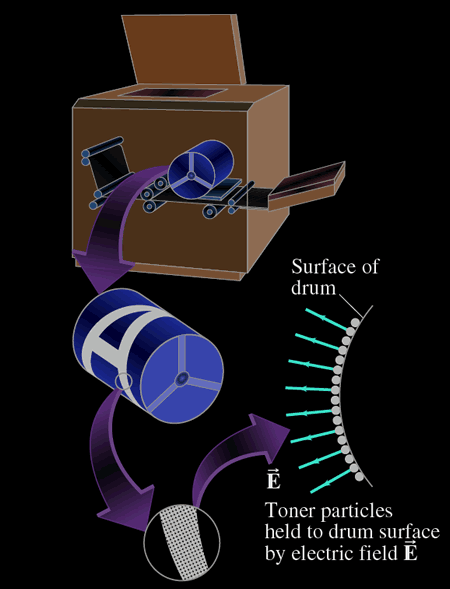
Aluminum is a conductor.
Selenium is a photoconductor, it is an insulator in the dark and
a conductor when exposed to lightlight.
So, a positive charge deposited on the Selenium layer will stay there.
However, when the drum is esposed to light, electrons from the aluminum will pass through the conducting selenium and neutralize the positive charge.
2. Imaging the document on the drum
3. Fixing the toner
4. Transferring the toner to the paper.
Multimedia Physics Animations
HyperPhysics
Science Joy Wagon
Atomic Theory
Bohr's Atom
More fun
The Applet Collection
Electrons in Orbit
The Physics of:
Electroplating
Dennis Kunkel Microscopy
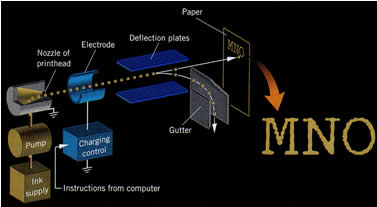
Xerography I, II
A Laser printer
Electromagnetic Field Lines
Millikan's Oil Drop Experiment