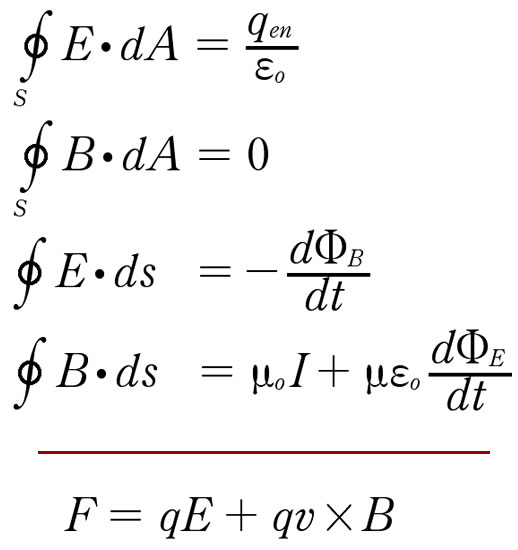Faraday's
Law of Induction
Electromagnet Induction.mov (106 MB)
1791-1867

So far we have studied
Electric Fields produced by
stationary charges
and
Magnetic Fields produced by
moving charges
What happens when Magnetic Fields vary in time?
wmv
What is
ElectroMagnetic Induction?
Why was Faraday's discovery so important?
ElectroMagnetic Induction?
Why was Faraday's discovery so important?
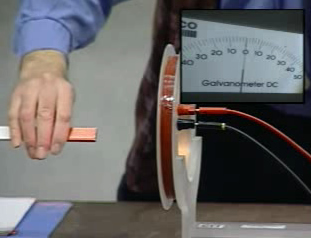
Faraday's Experiment
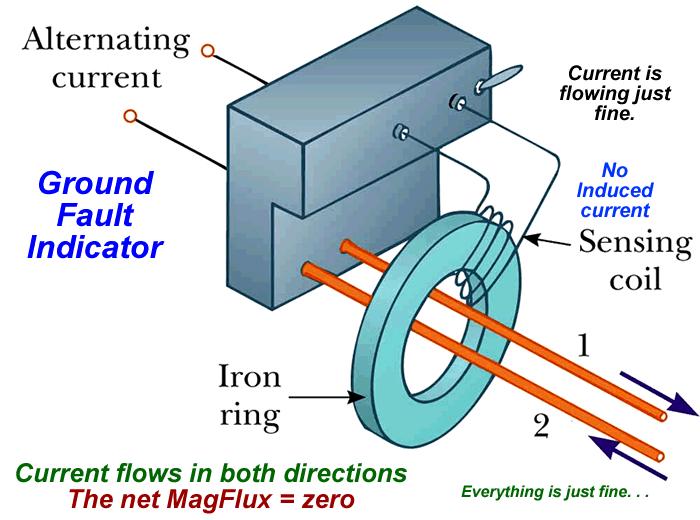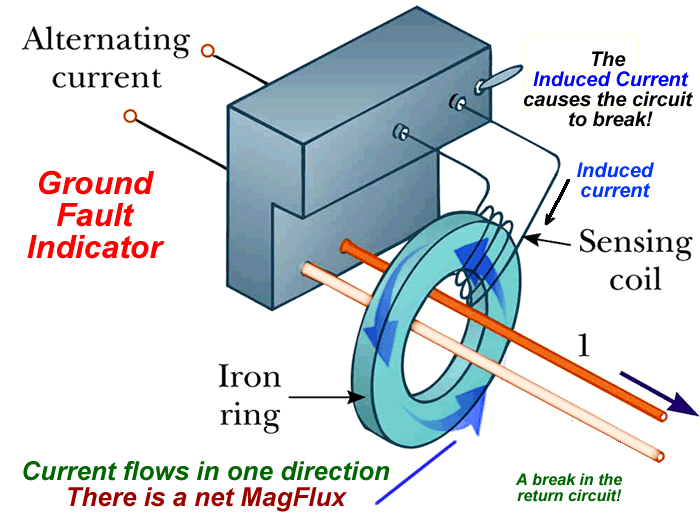
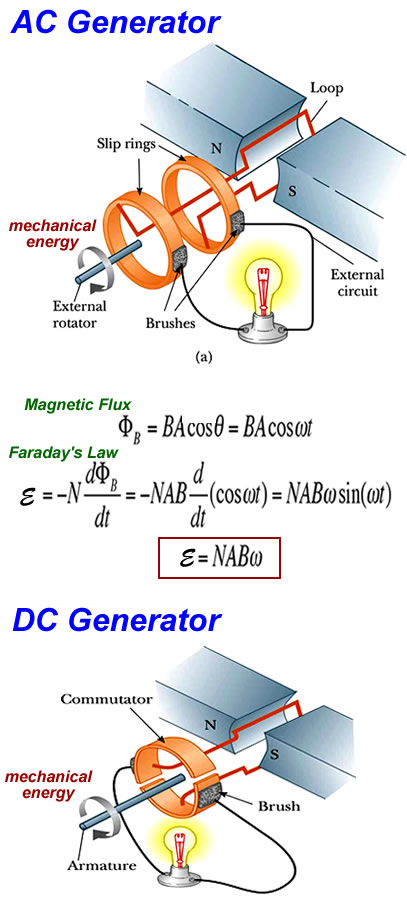
An electric current can be induced in a circuit by a changing magnetic field
click on the switch
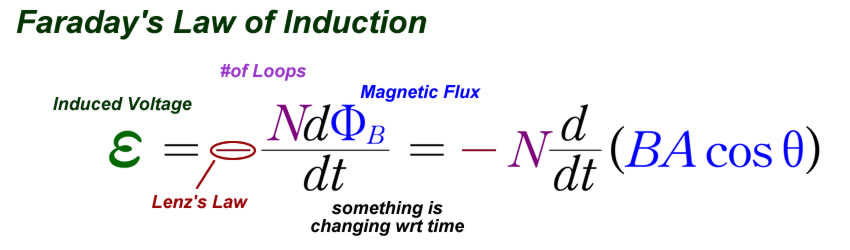
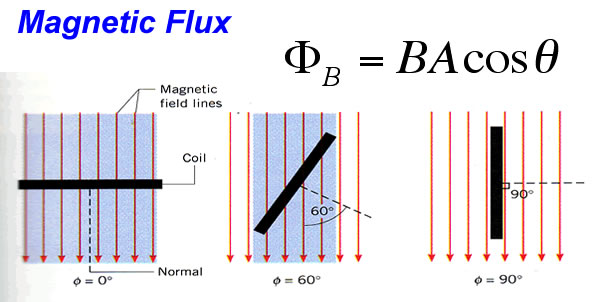
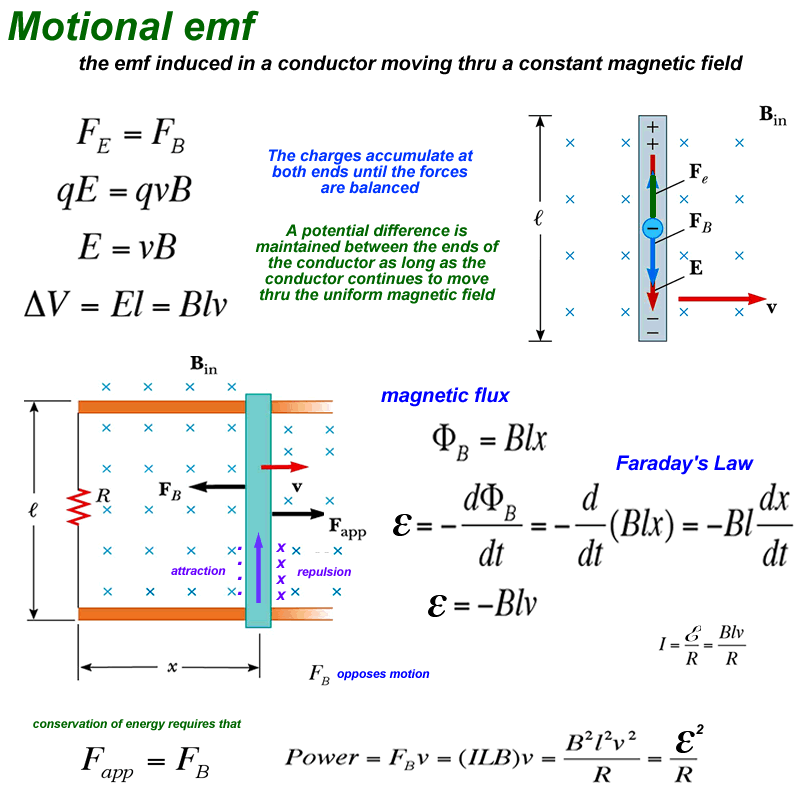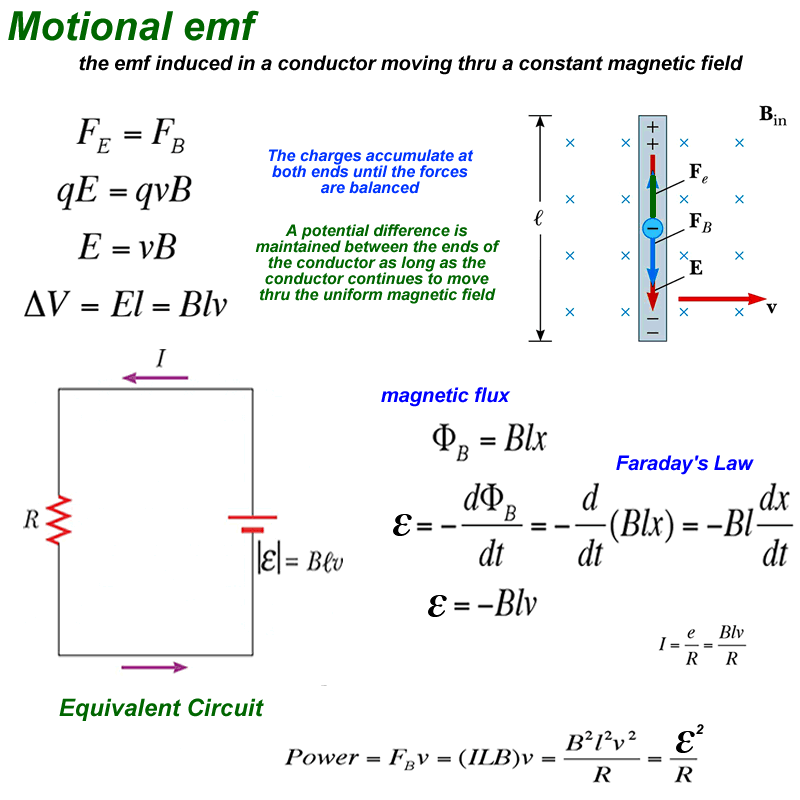
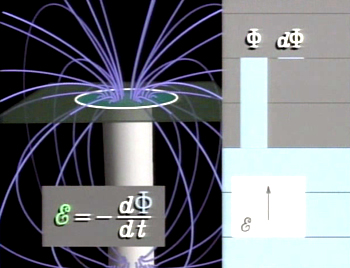
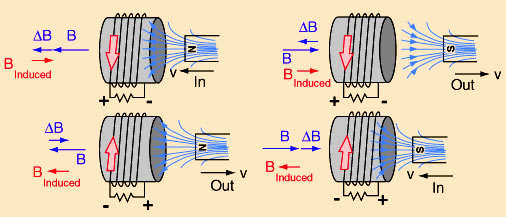
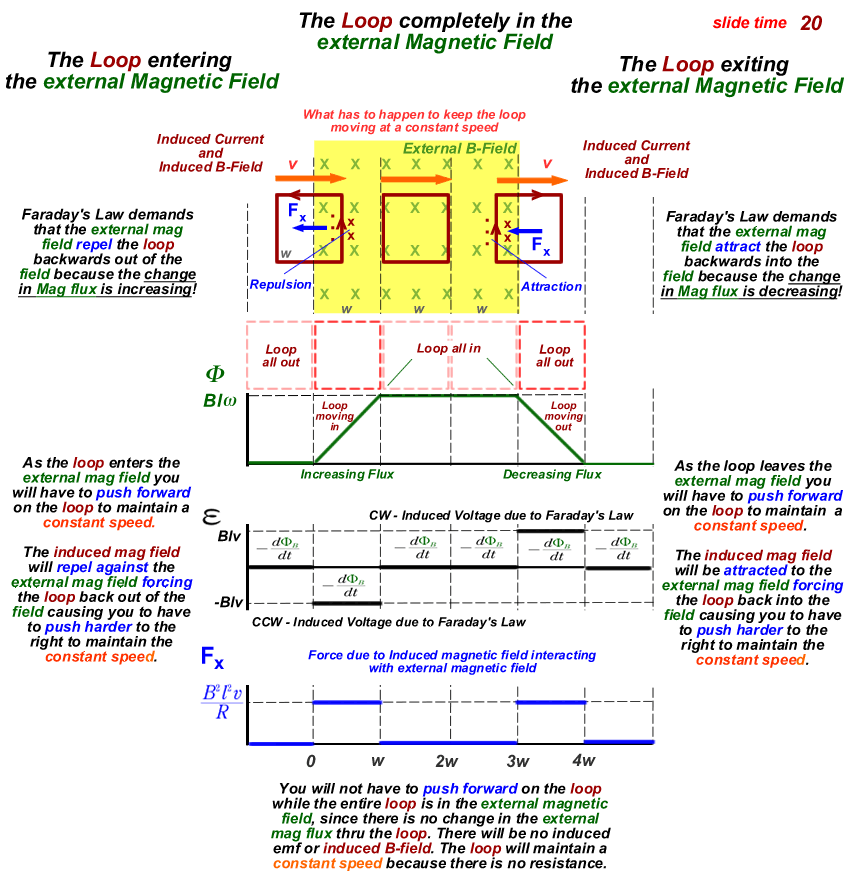
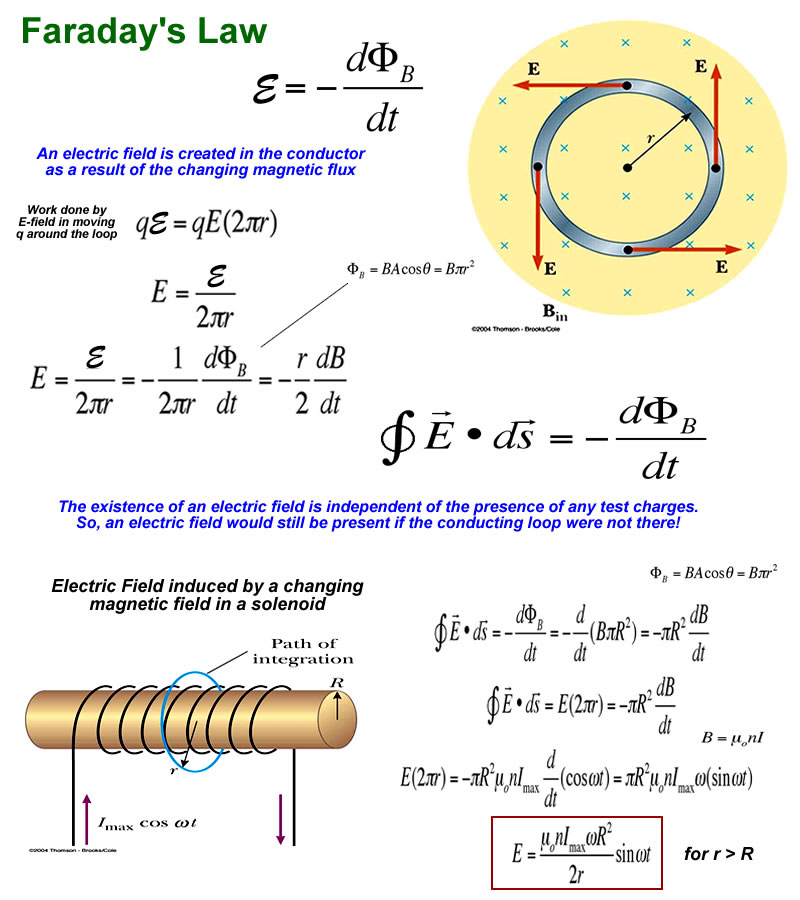
The induced emf in a circuit is directly proportional to the time rate of change of the magnetic flux through the circuit.
Watch the magnet as it enters the area of the super-cooled copper ring and as it leaves.
MIT

Faraday and the Law of ElectroMagnetic Induction
that creates a magnetic field that opposes
the change in magnetic flux through the loop.
Faraday's and Lenz's Law
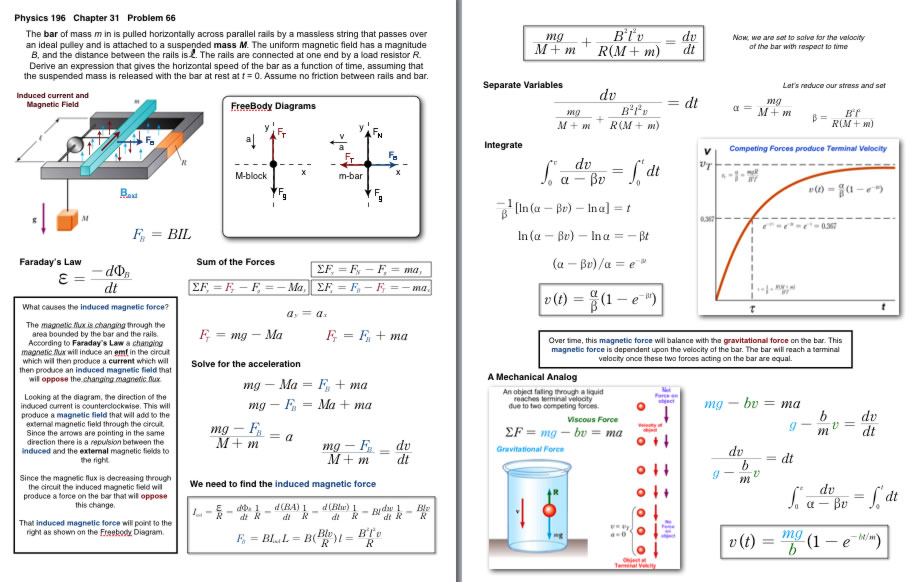
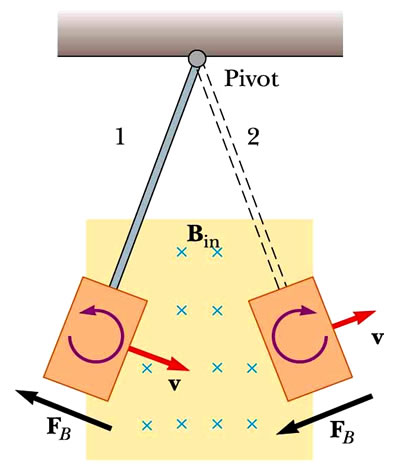
Faraday's Law and Terminal Velocity
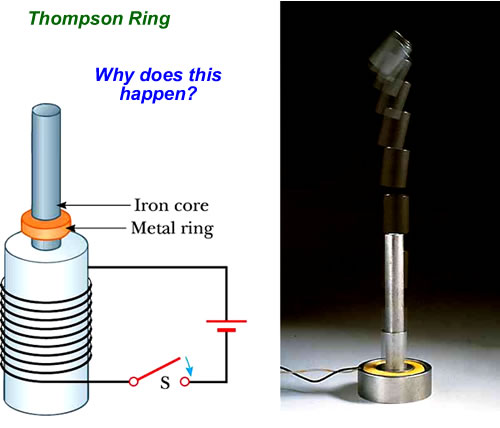
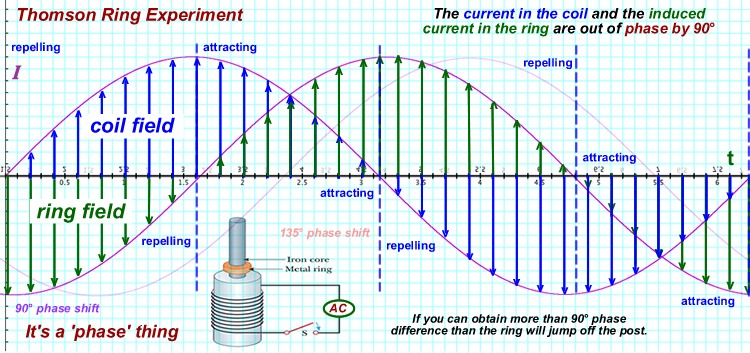
Why does the metal ring jumps off the center post?
Is Faraday's Law in play here?
Is it because of Lenz's Law or is there another principle at play here?
Hybrid Cars and Regenerative Braking
The greatest benefit of the gasoline engine is
the high energy density of gasoline, on the order of 12,000 Wh/kg,
in contrast with the much lower energy density of batteries, on the order of 500 Wh/kg.
This allows the much greater range of vehicles run on gasoline engines. The benefits of electric motors include high torque at low speeds, the absence of on-board emissions, and regenerative braking.
-- Karen Burke

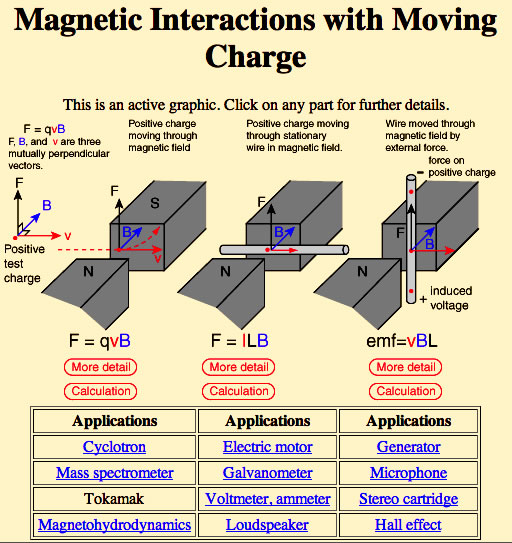
Gauss's Law
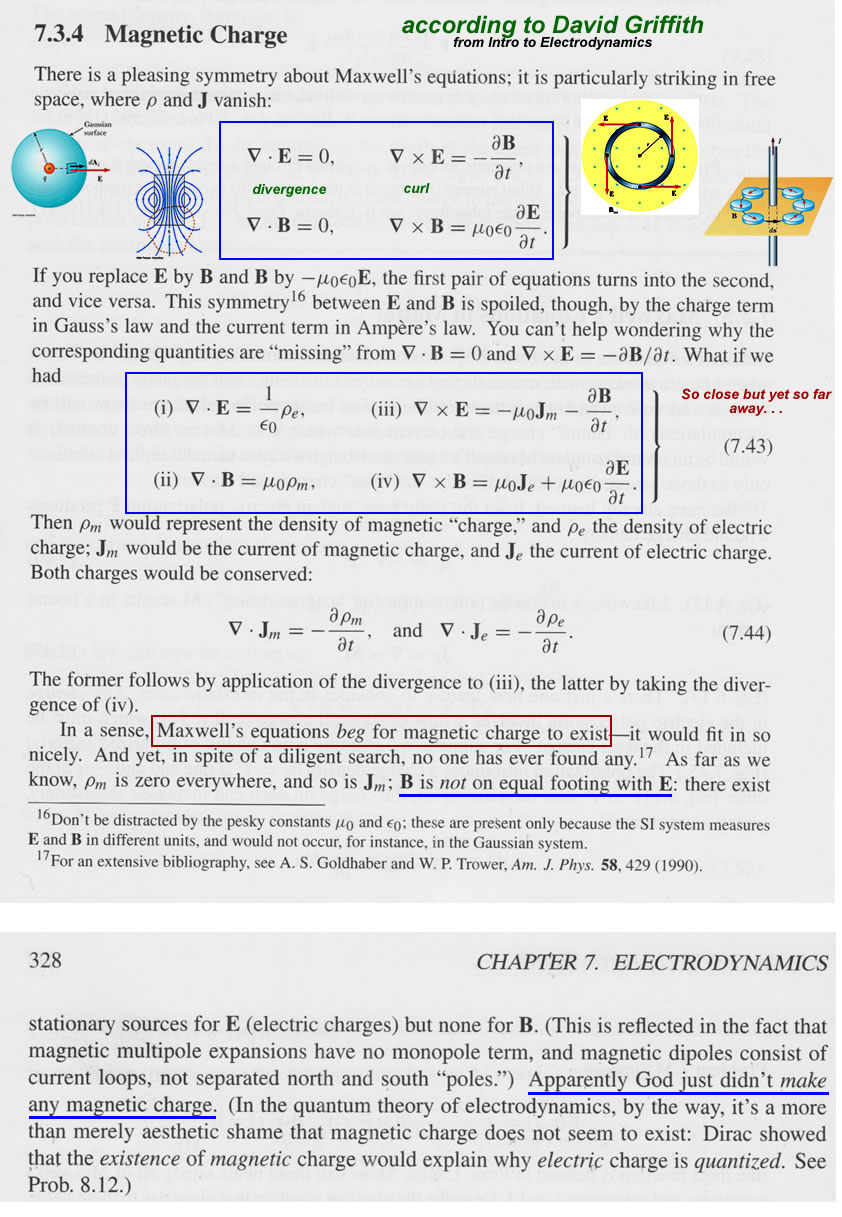
Gauss's Law of Magnetism
Faraday's Law
Ampere-Maxwell Law
Lorentz Force Law